Environmental Management
Environmental Management is essential for the Company, since its businesses directly impact the environment and society, from changes in land use and biodiversity, in the implementation phase of its projects, to the use of materials and natural resources, in operations, in addition to the generation of waste, emissions, effluents and noise.
Aware of its environmental commitment, Copel prioritizes renewable sources in the activities of electric energy generation, whose energy matrix of the generating park is predominantly hydraulic and wind.
The rationalization of the use of materials, energy and other natural resources is evidenced in the aspects of administrative and operational eco-efficiency, as well as water management. Concern about the environmental impacts of operations is demonstrated by environmental preservation and care for biodiversity.
Management of the environmental dimension at Copel is carried out based on the identification of risks, impacts and opportunities, proposition of improvements, as well as the definition of goals that help to compose indicators for integrated management, in accordance with the guidelines of the Sustainability Policy – Environmental Chapter.
Environmental studies are carried out for each project as part of the licensing process, at intervals that vary according to the complexity of the work. The results support specific environmental programs, which, in addition to being mitigating and compensatory, aim to achieve eco-efficiency, preserve biodiversity and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The Company manages the ISO 14001 Certificates – Environmental Management Systems in the context of energy generation in hydroelectric plants whose operations and maintenance are 100% controlled by Copel. Using this premise, around 77.8% of plants are certified.
The corporate guidelines for environmental management are guided by the voluntary commitments assumed and are provided for in Copel’s Sustainability Policy, unfolded in internal rules.
In addition to the licensing activities carried out in each of the businesses, Copel maintains a series of environmental programs related to the mitigation and compensation of negative impacts, as well as the enhancement of positive ones.
Climate Change management is a key element for the electricity sector, whether through adaptation, through the modernization of assets, or through mitigation, through the decarbonization of operations, thus reducing operational and financial risks.
The company’s environmental guidelines, applicable to its own employees, outsourced workers and suppliers, were built based on the concepts of eco-efficiency, which advocate the development of projects that properly use natural resources and allow the dissemination of good practices and company values.



Governance and responsibilities in Copel’s Environmental Management
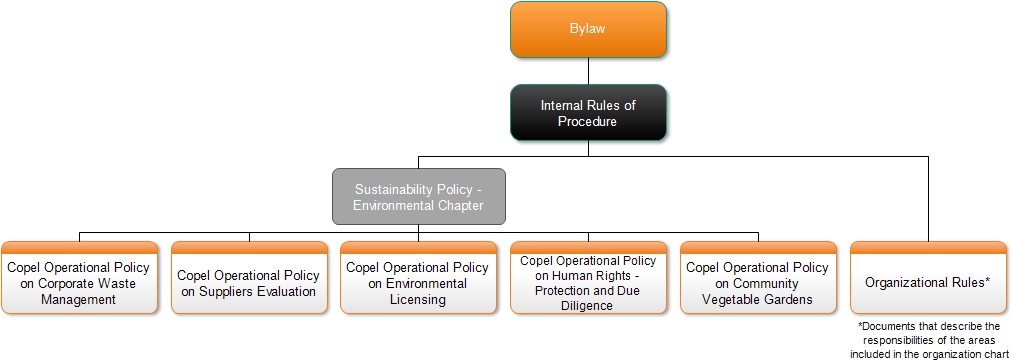
Copel organizes its operating rules based on normative documents that range from corporate guidelines to operational procedures for each area. In this context, the Bylaws define the purpose, operation, organic structure of Copel and the duties of the various statutory bodies. The Internal Regulations formalize the responsibilities, functioning and attributions of the rules contained in the Bylaws and in the legislation that governs the Company’s activities for all Copel’s collegiate bodies.
Regarding environmental management, the Sustainable Development Committee (CDS) is responsible for evaluating and monitoring the Company’s performance and the execution of projects that improve its practices, in accordance with its Internal Regulations. Under the optimal risk management framework, the Statutory Audit Committee (CAE) is responsible for evaluating situations in which the existence of unacceptable risks related to any of the Company’s activities is suspected, as well as the risk management system. Both committees report monthly to the Board of Directors on the main points addressed within the scope of the topics under their responsibility. It is the responsibility of the Board of Directors, in accordance with the Bylaws, to ensure that the Company carries out its activities in accordance with the bylaws and applicable legislation, providing solutions for sustainable development, thus ensuring its perpetuity.
Copel Policy Standards (NPCs), also called Corporate Policies, establish the direction for decision-making on specific matters, bringing the guidelines issued by the Board of Directors for each topic.
In terms of environmental management, the Sustainability Policy (NPC 0303) provides general guidelines that guide the positioning of businesses. The document is divided into chapters, the first chapter being Environmental (Copel’s Environmental Policy). Thus, in the environmental sphere, the policy provides guidance for action and decision-making, determines the provision of periodic training so that employees, suppliers and other interested parties understand the impacts of their activities on the environment, in addition to providing guidance the main responsibilities of the organization’s internal rules.
Internal standards are the direct consequences of corporate policies, containing responsibilities and rules. Copel Organizational Standards (NOCs) describe the purpose, main duties and hierarchical organization of a body in the Company, as well as the processes it executes.
Due to its complexity, responsibility for environmental management is shared between several areas. It is defined in the NOCs of areas of Copel Holding, Copel Geração e Transmissão and Copel Distribuição, as shown in the organization chart below:
Copel Administrative Standards (NACs) establish the rules for specific subjects. Currently, there are five NACs directly related to environmental management: Corporate Waste Management; Environmental Licensing; Suppliers evaluation; Human Rights: Protection and Due Diligence; and Community gardens; in addition to the NACs that are indirectly related to the subject.
For operational activities, there are Administrative Procedure Instructions (IAPs) and Technical Procedure Instructions (ITPs), which establish how administrative or technical activities must be carried out in accordance with the rules defined in corresponding standards.
Finally, the Supplier Manual is made available to suppliers, with specific environmental guidelines and directives for this interested party.
Indicators and Targets
The environmental targets of Copel are set through commissions composed by representatives of the Company’s directorates, and are developed based on the Company’s history, seeking to make better use of resources, minimize impacts and meet the economic analysis.
Each commission defines the values, the time frame and the way of conducting these goals, which are submitted to approval by the Company’s top management, with periodical monitoring of performance, and are valid for all processes, and are related to the performance of employees and of top management.
The main drivers for these goals are the Sustainable Development Objectives (SDO) and best market practices.
With the purpose of monitoring good practices and environmental management quality, Copel adopts a series of indicators, periodically monitored by the environmental areas of the Company, among which the following stand out:
- Atmospheric emissions and emissions of greenhouse gases (GEE);
- Waste;
- Consumption of natural resources (eco-efficiency: water, energy, fuels, paper);
- Environmental monitoring (ichthyofauna, effluents and vegetation)
Environmental Dimension Opportunities
Copel, through integrated risk management, seeks to reduce negative environmental impacts and maximizing positive impacts by using technology and prospecting opportunity.
The Company conducts environmental studies for power transmission undertakings, identifying the path of less impact, avoiding protected areas and using technology such as cable launch by drones, which avoid the need for suppressing vegetation for opening access in the woods. In energy generation, the Company has been seeking new sources, such as wind and solar.
In the distribution business, the Company implements compact grids, so the lines will interfere as little as possible with forest coverage, and also keeps the Urban Forest Program, with the purpose of harmonizing grids and vegetation of cities, supplying seedlings of smaller-size native species for covering roads and squares with vegetation.
Moreover, it has advanced in distributed generation that allows for better use of resources and increased operating efficiency, since it reduces energy loss and the response time of eventual disconnections.

Impacts
The impacts are detailed in environmental studies conducted according to regulatory requirements and whose results serve as basis for development of action not only for mitigation, but for preservation or recovery, conditions of the licensing process.
The main environmental impacts identified in the projects for implementation of undertakings are related to use of the soil, change of biodiversity, change of water availability, among others.
For diminishing the impact, Copel monitors and performs rescue of the flora and fauna; acts in the preservation and recovery of Permanent Preservation Areas (APPs); forest recomposition; in the archaeological monitoring and rescue, among other actions.
The initiatives are mostly executed in the implementation stages of the undertaking, and may unfold into the operations phase
Once in operation, the impacts are of a different class, such as generation of waste, air and water quality of reservoirs and emission of noise.
With the purpose or reduce, mitigate and compensate the impacts caused by installations, Copel keeps a series of environmental programs destined to identifying and monitoring interference of the Company’s processes, as well as of its suppliers and partners.
Risk Management
For reducing or minimizing risks, Copel invests in monitoring and in developing actions that allow a more efficient operationalization of generation, transmission and distribution processes.
Among the main environmental risks related to Copel’s business, we may mention those referring to the implementation and operation of undertakings such as power plants, power lines and substations.
Some aspects considered involve community mobilization, change of use of soil, climate changes, change of business activity, environmental impacts on biodiversity as well as those related to severe adverse climate that may cause accidents between electric power and the population.
Management of implementation and operation is carried out by strictly monitoring the process of licensing and implementation of undertakings, through project methodology, managing indicators, goals and targets.
Supply Chain Management
As a mixed economy company, Copel is subject to Federal Law 13.303/16 and the Internal Regulation of Bidding and Contracts, which restrict supplier selection actions. However, in addition to the legal obligations, the Company uses, as main criteria in hiring suppliers, compliance with labor legislation and respect for human rights, fiscal good standing and environmental commitment.
Copel is always attentive to environmental issues, and for this reason it includes specific clauses on this subject in the bidding notices, contractual clauses, supplier registration manuals and in the Code of Conduct, in addition to standards and technical manuals permanently available to interested parties on the organization’s website.
In case of negative impacts practiced by suppliers that violate the contractual instrument, the contract manager has the duty to evaluate the pertinent administrative sanctions that may be warnings, and/or fines, contract termination, and/or temporary suspension (independent administrative process).
Both in the certification of Copel GET suppliers and in the awarding of the best Copel DIS suppliers, one of the factors evaluated is compliance with the clauses referring to environmental criteria in the contracts.
Items such as environmental licensing certificates, certificates of origin of inputs, among others, are checked, from selection to the end of the life cycle of the contracts, when pertinent to the contracted object.
In the on-site inspections of Copel DIS contracts or for Industrial Evaluation of manufacturers of materials and equipment, verification items referring to respect to the environment are included, such as adequate waste disposal, for example.
Conduct Code

Supplier Management
Copel is always paying attention to environmental questions and therefore, it includes specific provisions on this theme in its contracts. If there are negative impacts practiced by suppliers that violate the contract, the contract manager has the duty to assess the pertinent administrative sanctions, which can be warnings and/or fines, termination of contract and/or temporary suspension (independent administrative process).
Both in the certification of Copel GET suppliers and in the awarding of the best suppliers of Copel DIS, one of the factors assessed is conformity with provisions referring to environmental criteria of contracts.