Materiality
The Company’s Materiality process is developed based on the survey and processing of data on issues relevant to Copel (Holding Company) and its wholly-owned subsidiaries, with the approval of the Board of Directors, whose result serves as support for the preparation of the Strategic Planning and the Integrated Report, being, therefore, fundamental to the conduct of the Company’s business, in addition to considering the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
Copel uses the guidelines of the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) to prepare its performance indicators related to sustainability practices, and the methodology of the International Integrated Reporting Council (IIRC) to structure its Integrated Report.
Both methodologies are considered best practice in stakeholder accountability and are widely used by companies that report on economic, environmental, social, and governance aspects. As part of the preparation process of these types of reports, the materiality process is presented within these methodologies in a similar manner, and its result is the backbone of Copel’s Annual Reports.
According to GRI, material topics are those considered important because they reflect the organization’s economic, environmental, and social impacts, or influence the decisions of stakeholders. The prioritization (stakeholder expectations x company impact) of these relevant topics results in the Company’s material topics. The main criterion, therefore, for defining material issues is impact, and the defining characteristics are frequency and severity.
The IIRC approach is broader, that is, the material issues are those that affect the organization’s ability to generate value from its capitals (financial, manufactured, intellectual, human, social and relationship, and natural). The prioritization of the themes is carried out with the analysis of the magnitude of their effects, which results in the Company’s material themes.
Copel’s Materiality Reports are prepared based on available methodologies, as well as on studies about the recurrence of the material themes reported by the most relevant companies in the sector, both in the domestic and foreign markets.
It is worth mentioning that Copel periodically reviews the materiality matrix in order to identify the most relevant topics for the Company and its subsidiaries, according to the context of the electricity sector, global trends, and the economic and social scenario.
Materiality Process
Material themes represent the most significant impacts of a company in the economic, environmental and social spheres. To reach its material themes, the Company carries out the Materiality Process every two years, with annual reviews. This materiality cycle was conducted 100% by Copel specialists.
Copel completed its most recent materiality process in 2023, with the support of several areas and the participation of all businesses. To do so, it was based on the recommendations of the international GRI Standards (GRI3: Material Themes 2021). In the end, Copel’s material topics were approved by the Board of Directors, which is the Company’s highest level of Governance. The complete process is valid for the period 2023 –2025, with annual reviews planned.
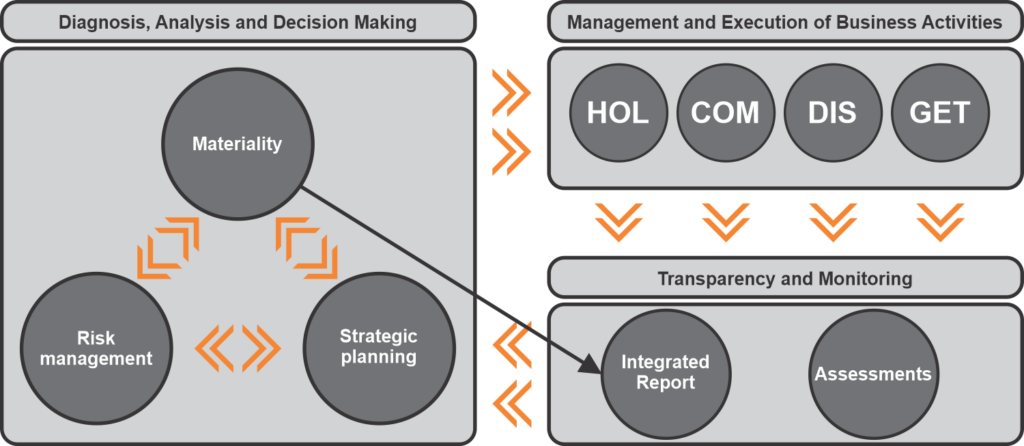
Material themes are a fundamental subsidy for the Company’s strategic planning, indicating the action priorities to be disseminated across all Copel areas and operations. Therefore, they serve as an important guide for the company. Furthermore, materiality is directly related to Copel’s risk management, as it uses inputs from existing risk management processes and provides results that directly contribute to such processes.
Material themes also guide the Integrated Report and Social and Environmental Reports, as the content and organization of the documents are based on materiality.
The image illustrates the role of materiality at Copel:
Stakeholder consultation
The latest materiality process represents a leap in quality for Copel. Firstly, it was one of the largest consultations with internal and external stakeholders (groups that impact or are impacted by Copel, such as customers, employees, suppliers, investors, among others) ever carried out by the Company. There were 6,905 participants from different segments, with emphasis on Copel customers: 3,595 respondents, representing 276 municipalities in the state of Paraná.
| Group | Answers |
| Customers | 3.595 |
| Communities* | 25 |
| Board of Directors, Executive Officers and Presidency | 18 |
| Own Employees | 1.755 |
| Empregados Terceirizados | 459 |
| Sector Entities | 6 |
| Interns | 133 |
| Suppliers | 314 |
| Investors | 552 |
| Regulatory Bodies** | 3 |
| Corporate Interests*** | 10 |
| Society**** | 35 |
| Total | 6.905 |
* Communities: leaders of the communities with which Copel interacts were consulted;
** Regulatory bodies: three responses were received from representatives of the National Electric Energy Agency (Aneel);
*** Shareholdings: in 2023, Copel had 26 shareholdings, represented by 12 managers. Of these, 10 participated in the consultation.
**** Society: members of institutions representing society were consulted, such as universities, schools, NGOs, among others.
Double materiality
For the first time, Copel carried out double materiality, in line with the best market practices. Double materiality consists of the joint analysis of ESG aspects with their financial impacts on the Company, strengthening corporate strategy and risk management. From there, the prioritization of some themes, such as population safety, was accentuated.
Considering the double materiality, 34 topics were considered material for the Company, with some distinctions in the level of criticality for the business.
To facilitate practical use, as per GRI guidance, the themes were organized into ten groups:
- Population Safety: mainly related to the safety of dams and reservoirs, as well as the prevention and monitoring of accidents involving the population with electricity. The topic has an important link with climate change, as extreme weather events, such as more intense and frequent storms, floods or droughts, affect energy generation and distribution operations and can have impacts on the safety of the population.
- Customer Satisfaction: is directly linked to the economic and financial results and the Company’s reputation.
- Wellbeing, Health and Safety for the Workforce: involves taking care of the health, safety and quality of life of workers, reducing and monitoring the severity rate of accidents involving employees and contractors.
- Social Commitment: considers commitment to communities, human rights, engagement with stakeholders and social responsibility.
Environmental Commitment: considers climate change, commitment to biodiversity, eco-efficiency, water resources management and environmental responsibility. - Transformation of the Energy Sector: includes energy efficiency, operational efficiency, electrification, generation of clean electrical energy, innovation, investments in electrical energy distribution and transmission infrastructure, new business opportunities, and cyber and information security.
- Economic-Financial Performance: reflects the Company’s financial health and the degree of success achieved with the capital invested, therefore allowing interested parties to evaluate the use of resources, including business efficiency, and the factors that influenced it.
Sustainable Supplier Management: involves hiring, monitoring suppliers in ESG aspects, due diligence, guidance and monitoring of suppliers. - People Management: involves investment in human capital, professional and personal development programs, organizational climate, training for own and outsourced employees, as well as remuneration policies, benefits and relationships with unions.
- Corporate Governance: mainly covers the principles of the governance model; the structure and composition of the Company’s governance; the practices and mechanisms that guarantee the effectiveness and quality of this governance; the way the compliance process is carried out and its performance; integrated corporate risk management and matters related to the regulatory environment.
The matrix below aims to illustrate the grouped themes of double materiality.
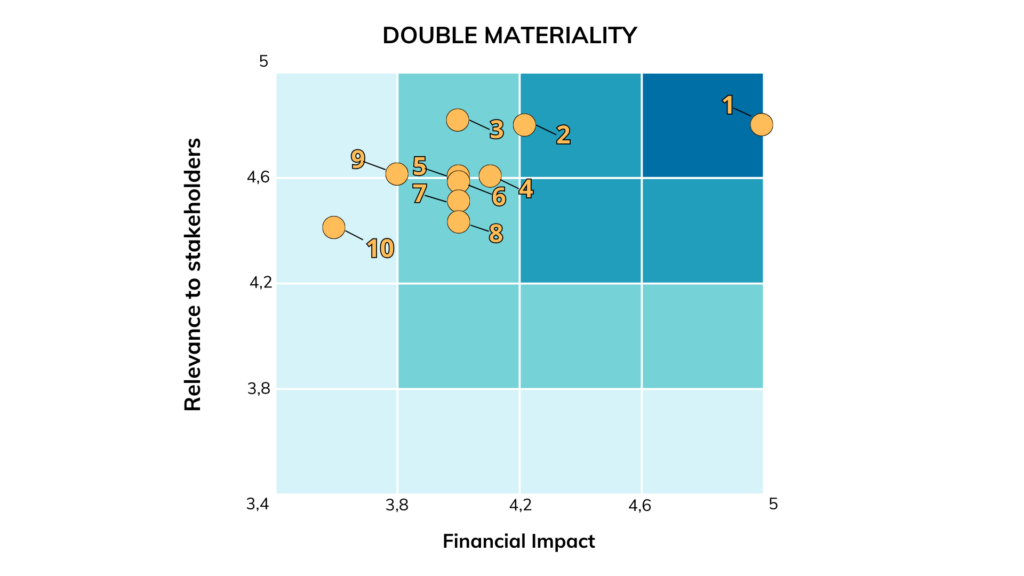
They all have high relevance, but the closer they are to the top right corner (or the darker the shade of blue), the more significant the group’s relevance is, both for interested parties and in terms of financial impact.
Subtitle:
1. Population Security
2. Customer Satisfaction
3. Wellbeing, health and safety for the workforce
4. Social Commitment
5. Energy Sector Transformation
6. Economic-Financial Performance
7. Sustainable Supplier Management
8. People Management
9. Corporate Governance
10. Environmental Commitment




