Fish Study Experimental Station
Fish Study Experimental Station – EEEI
EEEI was built shortly after the start of operation of HPP GNB, in 1992, being completed in 1993 and its creation occurred as part of the environmental licensing process for the implementation of this plant.
The Station’s activities have always been focused mainly on species of interest for conservation, with emphasis on the species Steindachneridion melanodermatum, known as surubim-do-Iguaçu.
The occurrence of a new species of the genus Steindachneridion, endemic to the Iguaçu river basin, was recorded for the first time in 1991, indicating that the species occurred downstream of Salto Segredo, being confirmed in 1994.
EEEI verified the opportunity to work with a rare native species and influenced by the plants in the Iguaçu basin, and began working on the development of experimental fish farming, capturing specimens of surubim-do-Iguaçu in the lower Iguaçu river basin, to form the breeding stock.
The work of Copel and its partners enabled the development of captive breeding and reproduction technology for this important species, representing a pioneering study and serving as the basis for several scientific studies to be developed at the site.
Aiming to maximize the genetic variety of surubim-do-Iguaçu fry, the entire breeding stock received identification chips, which allows crossbreeding to be controlled, which, in turn, allows maximizing the genetic variety of the fry, something important in a fish farm. for environmental conservation purposes.
Reproduction and Repopulation Actions
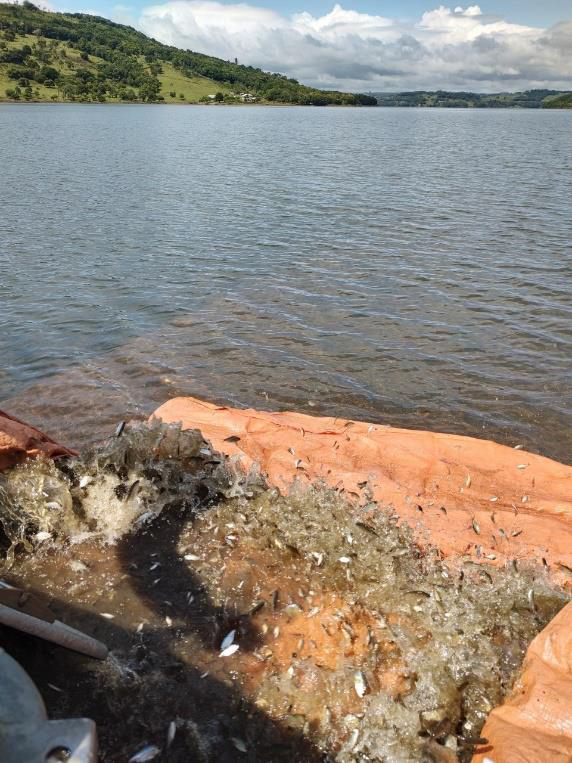
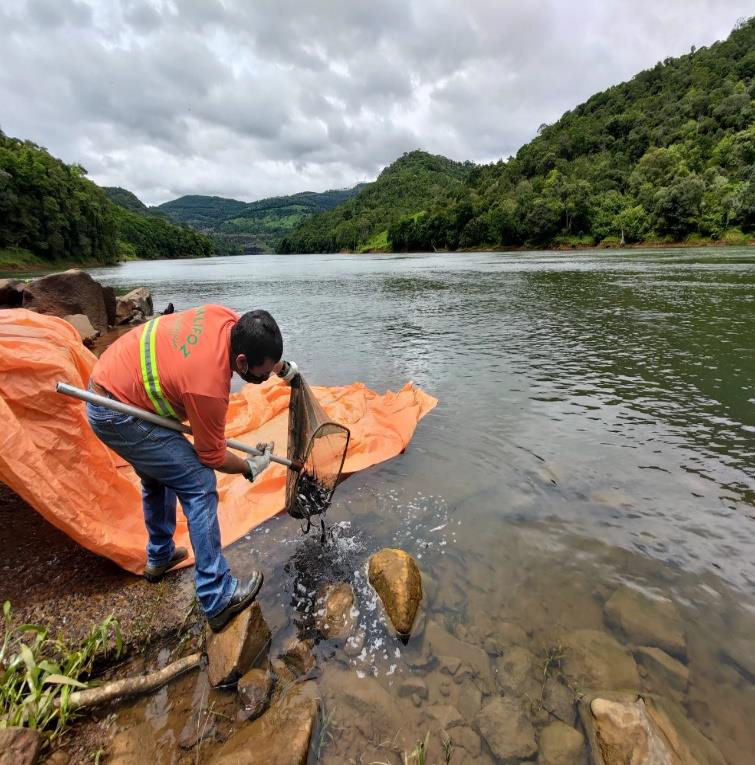
With reproduction and repopulation actions, Copel aims to mitigate the impacts caused to ichthyofauna. The species used are those reproduced in EEEI, in captivity, and the controlled release of individuals of native species helps the natural populations of these species.
Reproduction and repopulation include the following activities:
- Breeder capture and maintenance.
- Fertilization
- Fish Hatchery.
- Release.
The reproduction activities of the Iguaçu surubim occur in the hottest months of the year, normally starting in September, continuing until February of the following year. After the fry reach the ideal size for release, according to each breeding batch, restocking activities can be carried out from October to March of the following year.
Other activities
EEEI professionals are also responsible for carrying out ichthyofauna rescue activities when machine downtime occurs at plants in Paraná and for environmental inspection actions at the Company’s hydroelectric projects, monitoring water quality and the multiple uses of reservoirs.
In addition to these activities, the EEEI team has also undertaken searches for other species of conservation interest listed in the National Action Plan for the Conservation of Aquatic and Semi-Aquatic Fauna of the Baixo Iguaçu Basin (PAN Baixo Iguaçu), in which Copel is a of collaborators. The PAN Iguaçu, successor to the PAN Baixo Iguaçu, includes 13 species of fish found in the Baixo Iguaçu basin, including the Iguaçu surubim, a species targeted by Copel for conservation actions.
Actions planned for 2025
For 2025, the activities planned for restocking involve breeding the species Surubim-do-Iguaçu – Steindachneridion melanodermatum and Lambari – Astyanax bifasciatus and then releasing the fry. Breeding takes place in the warmer months of the year, beginning in September and continuing until February of the following year. After the fry reach the ideal size for release, according to each breeding batch, restocking activities can be carried out from October until March of the following year.
For 2025, the plan is to continue responding to environmental emergencies and rescuing fish at power plants and preparing for the 2025 reproductive cycle, as well as implementing the action plan for reproduction, restocking and including new endangered species in the program already carried out at the fish farming station.

Restocking Results
Species | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 | 2024 |
Lambari | 75,000 | 30,000 | 38,000 | 8,000 | 72,900 | 0 |
Surubim do Iguaçu | 6,220 | 2,301 | 2,445 | 12,919 | 1,789 | 561 |